Newton’s Third Law and Bernoulli’s principle
Principle of FLights
What is Newton’s Third Law?
Newton’s Third Law of Motion states that for every action, there is an equal and opposite reaction. This means that any force exerted onto a body will create a force of equal magnitude but in the opposite direction on the object that exerted the first force.
This law explains how forces always come in pairs – action, and reaction. These two forces are always equal in magnitude, but they are directed in opposite directions.
Example of Newton’s Third Law Involving Aerodynamics
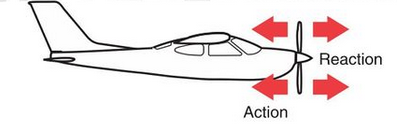
Airplanes
The motion of an airplane is a perfect example of action and reaction in aerodynamics. The airplane’s engines thrust air backward. In reaction to this action, the plane moves forward. This forward movement is the reaction to the action of the air being forced backward by the engine.
What is Bernoulli’s principle?
In the simplest terms, it states that as the speed of a fluid (air or liquid) increases, its pressure decreases. This means that if you have a curved surface that forces air to move faster over the top than the bottom, you create a difference in pressure, which generates lift. This is known as the “Bernoulli effect.”
Now, let’s apply this principle to the flight of airplanes. As an airplane moves forward, air flows over its wings, which are curved on the top and flat on the bottom. This creates a difference in the speed of the air flowing over the top and bottom of the wing, with the air on top moving faster than the air on the bottom. According to Bernoulli’s principle, this difference in airspeed creates a difference in pressure, with lower pressure on top and higher pressure on the bottom.
